In an extremely competitive market with ever-shrinking margins of error, efficiency in contract and supplier management emerges as a crucial factor for the success of any industry. This scenario becomes even more critical within the maintenance environment, where the quality of the product or service provided can vary significantly depending on the implemented contractual management practices.
Maintenance managers need to keep in mind that contract and supplier management is not just a matter of fulfilling legal obligations or managing supply relationships. It is a tangible strategy that directly influences the quality of industrial maintenance, acting as a competitive advantage that can distinguish successful companies from those that fail to maintain their operational standards at high levels.
But how can effective supplier management translate into operational impact and return on investment (ROI)?
ROI and Payback: KPIs to Unlock Business Growth
First and foremost, efficient supplier management enables the company to optimize its maintenance processes, minimizing delays and disruptions that can become extremely costly. Well-administered contracts ensure that both parties are aligned regarding expectations and deliveries, reducing the risk of misunderstandings that can lead to legal disputes.
And ROI in this type of situation is not just about financial return. It also involves building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, enhancing the quality of services, and consequently, customer satisfaction. Contract administration and efficiency in supplier management have a cascading effect that goes beyond the maintenance department, permeating the entire organizational structure and contributing to its sustainable growth.
In this article, we will delve into all these aspects, providing a comprehensive and practical guide for you, the maintenance manager, to navigate the complex landscape of contract and supplier management with safety and confidence.
Mechanical Failures: Best Practices for Prevention
Fundamentals of Contract Management
Before devising strategies, it is crucial to understand the legal principles that govern contracts to ensure the effectiveness of contract and maintenance supplier management. Contractual scenarios can vary depending on the laws of each country. In the United States, contractual regulations and laws are governed by common law principles, as well as statutory laws that can vary by state.
- Autonomy of Will: In the U.S., this principle is reflected in the freedom to contract. Parties generally have the freedom to negotiate and agree upon the terms of a contract as long as they are not illegal or against public policy.
- Binding Force of Contracts: This principle aligns with the concept of “meeting of the minds” in contract law. It emphasizes that once parties have reached an agreement and all essential terms have been defined, they are generally bound to fulfill their contractual obligations.
- Relativity of Contractual Effects: Generally, only the parties who are part of the contract have rights and obligations under it. Third parties who are not part of the contract typically do not have enforceable rights, with some exceptions (such as beneficiaries in certain types of contracts like insurance policies or trusts).
It’s important to note that while these principles are generally applicable in the U.S., there may be specific state laws and regulations that can impact the interpretation and enforcement of contracts. Additionally, certain industries or types of contracts may have specific statutory requirements or regulations. Legal advice from a qualified attorney is often recommended when drafting or interpreting contracts.
And for a maintenance manager, understanding these principles is crucial for several reasons:
- Clear Definition of Responsibilities: Contractual principles help clearly define the responsibilities of each party, which is crucial for effective maintenance management. They ensure that both the supplier and the client are aware of their obligations, thereby minimizing the chances of misunderstandings and disputes.
- Legal Protection: Understanding contractual principles provides a solid legal foundation for contract management, protecting the organization against potential litigation and adverse financial consequences.
- Operational Efficiency: A clear understanding of contractual terms and their implications aids in the effective coordination of maintenance operations, ensuring that resources are utilized optimally and maintenance objectives are achieved as planned.
- Relationship Management: The correct application of contractual principles also facilitates the management of relationships with suppliers and other stakeholders, contributing to long-term partnerships and improved operational performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: These principles help ensure that contracts comply with local laws and regulations, which is vital for avoiding legal penalties and ensuring uninterrupted maintenance operations.
For these reasons, education in contractual principles is a fundamental step for maintenance managers who aim to ensure a smooth and effective contract execution, aligned with organizational goals and local regulations.
How to Achieve Maximum Industrial Asset Availability
Best Practices in Contract Management
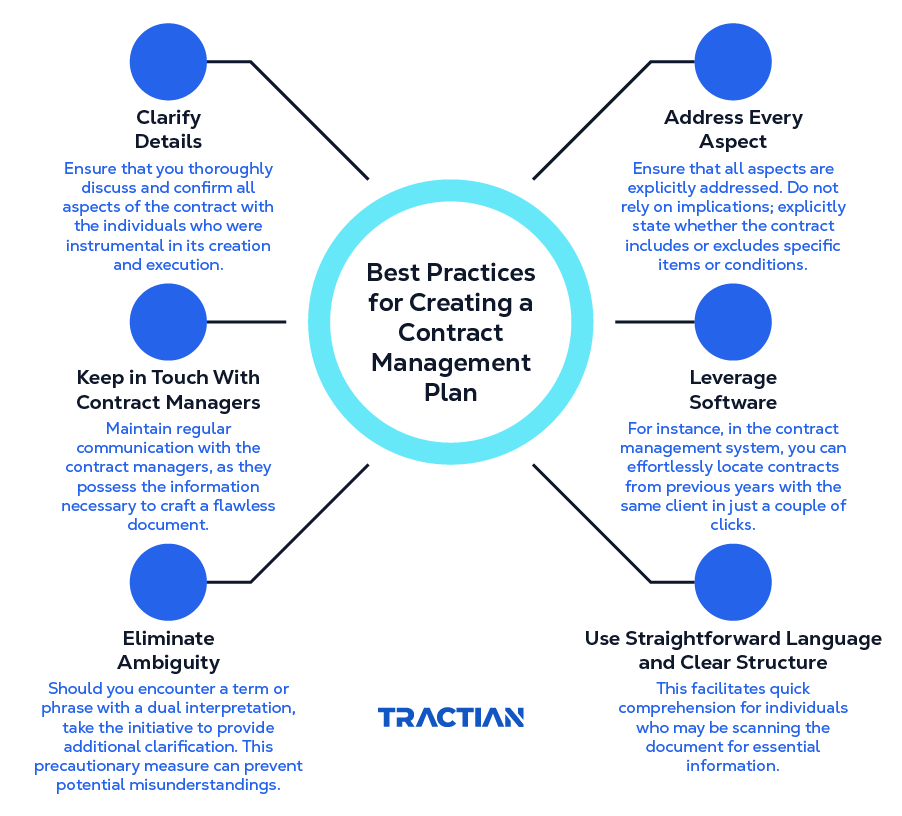
Implementing best practices is crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with contractual agreements. Some recommended actions include:
- Careful Drafting of Contract Clauses: Ensure that the clauses are clear, fair, and comprehensive.
- Creation of a Contract Management Plan: A well-developed plan can simplify the administration of complex agreements, making them more accessible and manageable.
- Standardization of Processes: Establish clear and consistent processes for the creation, execution, and analysis of all contracts.
Contractual Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Efficient risk management is a vital facet of contract management. Some strategies include:
- Identification and Assessment of Risks: Identifying potential threats and assessing their impact is the first step towards effective risk management.
- Development of a Risk Control or Elimination Plan: Creating strategies to control or eliminate risks, which may include accepting the risk when the cost of management exceeds potential losses, or transferring the risk, for example, through insurance.
- Preventative Mitigation: Adopting a proactive approach to minimize the likelihood of risk occurrence, as well as its potential impact on contractual and organizational objectives.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Conducting regular risk assessments and reviews of the mitigation plan to ensure that the strategies remain relevant and effective.
- Contract Auditing: Auditing is a process aimed at reviewing and analyzing contracts and related documentation to ensure compliance with agreed-upon terms and conditions, as well as applicable laws and regulations. This process can identify areas for improvement, potential cost savings, and ensure that both parties are fulfilling their contractual obligations.
The implementation of robust contract management practices and risk mitigation strategies can help ensure contractual compliance, protecting the organization against uncertainties, ensuring proper adherence to norms and regulations, and optimizing operational performance and business outcomes.
Supplier Management
The effectiveness of industrial maintenance relies not only on high-quality equipment or a specialized team but also on the ability to manage a complex network of suppliers. This section addresses the essential elements of supplier management and how it relates to other crucial aspects of maintenance.
Supplier Selection and Evaluation

The first step towards effective supplier management is identifying the best opportunities in the market. Procurement teams, responsible for selecting and evaluating partners, should adopt well-defined metrics and criteria to assess supplier performance, ensuring they meet all necessary specifications and requirements.
The goal here is to find the supplier that offers the most added value. Aspects such as reliability, quality of materials, and delivery track record are crucial in the decision-making process. This is particularly important for maintenance managers, who rely on qualified maintenance suppliers to keep operations uninterrupted.
Mobility: Remote Maintenance, Wherever You May Be
Building Partner Relationships: The Secret to Long-Term Success
Once suppliers are identified and deemed suitable, the next step is to develop and maintain a healthy relationship with these new partners. This involves the effective management of the current supplier base and also the ongoing search for strategic partnerships that can offer innovation in production, as well as cost savings in contracts.
Effective relationship management goes beyond mere business transactions and enters the realm of strategic partnership. Both parties should view themselves as collaborators in a mutual effort to achieve common goals. The relationship should be maintained through open communication, regular performance reviews, and contract renegotiations.
Integration between Contract and Supplier Management
For large-scale projects, the integration between those responsible for contract and supplier management is crucial. This functional collaboration can be the key to success in both administration and the production environment.
By aligning strategies and processes, these teams can act in a coordinated manner to identify and mitigate risks, optimize costs, and ensure that contractual terms are adhered to by all involved suppliers. This integration is even more critical for maintenance managers, who need to ensure that suppliers comply with established contracts.
In conclusion, supplier management is a critical area that requires a multifaceted approach. From selection and evaluation to the development of strong relationships, each step is crucial to ensure successful operations. By paying attention to these elements, managers not only optimize their operations but also strengthen long-term business and strategic relationships.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement
The pursuit of continuous improvement is a crucial pillar for any industry aiming to be competitive and efficient. Here, we will address strategies that focus on three fundamental areas: Performance Analysis and Benchmarking, Technology in Contract and Supplier Management, and Team Development and Training.
Supplier Performance Analysis and Benchmarking
Supplier performance evaluation is not an isolated action, but rather a continuous process. By using appropriate metrics and KPIs, maintenance managers can not only assess but also compare their suppliers’ performance against industry best practices. This benchmarking can reveal areas that need improvement and serve as a basis for negotiation and renewal of preventive and reactive maintenance contract terms.
Technology in Contract and Supplier Management
The use of technology, especially automation and monitoring systems, is becoming increasingly prevalent in supplier and contract management. These technologies can bring greater effectiveness and efficiency, helping to implement improvements and achieve cost savings in contracts. Technological solutions enable the monitoring of compliance with contract terms and clauses to be more transparent and easier to audit.
Team Development and Training for Contract and Supplier Management
For all these strategies to be effective, it is crucial to have a highly qualified procurement team. Investing in professional development and training not only enhances individual skills but also boosts the overall effectiveness of the team. Proper training can expand the team’s knowledge in both supplier performance evaluation and preventive and reactive maintenance contract management, making management more efficient.
Long-Term Strategies for Contract and Supplier Management
Efficiency in contract and supplier management is undeniably one of the pillars that support the success of industrial maintenance operations. Far from being a mere administrative formality, this is a complex business strategy that directly influences the quality, reliability, and effectiveness of maintenance operations.
The successful implementation of these practices not only ensures compliance with regulations and minimizes risks but also contributes to the establishment of long-lasting and mutually beneficial business relationships. This way, managers not only optimize their operations but also position their organizations for sustainable long-term growth.



