ESG - Environmental, Social, and Governance - is increasingly becoming the backbone of modern business and investment strategies. But what exactly is ESG, and why is it gaining such momentum in the corporate world?
At its core, ESG represents a set of standards for a company’s operations that socially conscious investors use to screen potential investments.
It encompasses a broad range of activities, from reducing environmental footprints to ensuring ethical governance.
But… Why does this matter more now than ever?
The current socio-economic climate demands that companies not only focus on profitability but also consider their impact on the planet and society.
Think of it this way: we’re not talking about a holistic approach that focuses on ‘doing good’ . It’s about something bigger, like sustainability and long-term growth.
And mind you: investors are taking note. More than 90% of the top S&P 500 companies now publish Environmental, Social, and Governance reports, and around 70% of Russell 1000 companies follow suit, according to McKinsey.
Now, more businesses are recognizing that incorporating those principles is crucial for their reputation, investor appeal, and resilience in an ever-evolving market.
So, in an industry-focused context, how can companies adapt and thrive while embracing these values? The answer lies not just in compliance but in embracing ESG as a strategic tool for innovation and sustainable success.
Understand it all in this article, where we dissect the concept. Keep reading!
The Environmental Aspect of ESG
The “Environmental” aspect of ESG zeroes in on how businesses interact with the planet. It’s about understanding and managing a company’s environmental footprint, addressing key issues such as climate change, resource depletion, waste management, and pollution.
This component emphasizes the need for sustainable practices and the reduction of environmental impact across all business operations.
Take, for example, the issue of climate change.
Companies are increasingly adopting measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
It’s an answer to a growing movement of consumers that had enough of climate abuse. According to PwC, 76% of consumers say they will stop buying from companies that treat the environment, employees, or the community in which they operate poorly.
But what does this mean for businesses? Initiatives like transitioning to renewable energy sources, optimizing manufacturing processes for energy efficiency, or investing in carbon offset projects.
Resource depletion is another critical area. Companies implement strategies like sustainable sourcing and circular economy principles to minimize the extraction of raw materials.
They recognize that conserving resources isn’t just environmentally responsible but also economically prudent.
Waste management and pollution control are equally crucial. Innovative waste reduction and recycling initiatives are being adopted to minimize environmental harm.
For instance, Coca-Cola Company has committed to making its packaging 100% recyclable globally and using at least 50% recycled material in its packaging by 2030.
Each of these efforts reflects the growing commitment of businesses to actively engage in practices that contribute positively to the planet’s health.
The Social Dimension of ESG
The ‘Social’ dimension of ESG puts the spotlight on how companies build and nurture relationships with their employees, suppliers, customers, and the wider community.
It’s about delving into the core of human interactions and values within the business context.
But what does this actually look like in practice?
Take a look at human rights and labor standards.
Companies committed to these principles rigorously ensure fair labor practices and safe working conditions, not just within their own walls, but throughout their supply chains.
Compliance, you think? Yes, but this is also about fostering a culture of respect and dignity.
Employee engagement is another crucial pillar. How do companies cultivate a workplace where every voice matters and everyone feels valued?
Some businesses are already actively embracing diversity and inclusion, creating environments where varied perspectives lead to innovative solutions and a more dynamic workplace - and they’re showing.
For example, some big tech companies already publish annual diversity reports, such as Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Meta.
And what about the communities these companies operate in?
It’s about being a good neighbor, engaging in social initiatives, and contributing positively to local development.
This holistic approach to the “Social” aspect of Environmental, Social, and Governance demonstrates that businesses are about more than profits, they’re about people.
Understanding Governance in ESG
“Governance” is the backbone of how companies operate internally. It’s about the integrity with which a company is run.
But what does good governance actually entail?
You see: it starts with corporate governance - the framework of rules and practices that guide company management.
It’s about ensuring that those at the top are acting ethically and in the best interests of their stakeholders.
How does a company ensure its leaders are accountable? This is where things like executive pay come into play, aligning compensation with the company’s long-term health, rather than short-term gains.
Audits and internal controls are equally vital.
They’re the checkpoints ensuring that everything is running as it should.
It’s about transparency, about making sure that there’s a clear, honest picture of what’s going on inside the company.
In its essence, governance is about building a foundation of trust and integrity, crucial for sustainable business success.
Why ESG Matters: The Importance for Businesses and Investors
So… Why does Environmental, Social, and Governance matter so much for businesses and investors? The main point we like to make is this: don’t face this concept as a mere trend, but as a crucial part of assessing a company’s future financial health and managing investment risks.
For businesses, this is a lens through which they can identify and mitigate risks that could have financial repercussions.
Think about it - environmental mishaps, poor labor practices, or governance scandals can not only harm a company’s reputation but also impact its bottom line.
On the flip side, strong practices can attract investors, enhance brand value, and drive long-term growth.
And mind you that investors are increasingly using ESG criteria to predict a company’s future performance.
According to the latest ESG Global Study by Capital Group, the majority of investors see Environmental, Social and Governance investments and portfolios as something positive:
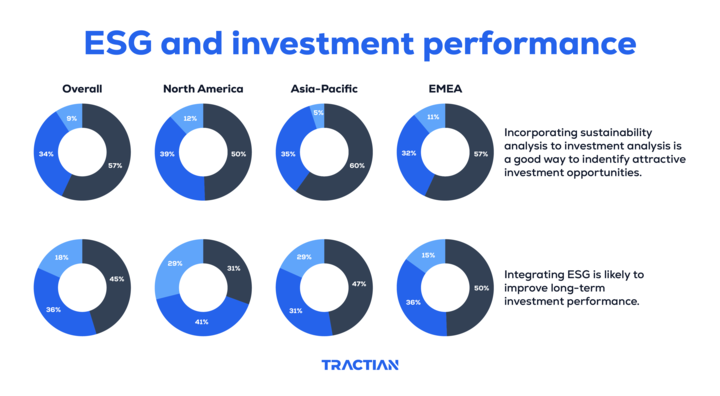
Companies with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance profiles are often seen as better positioned to withstand market turbulences.
For instance, over 50,000 European companies, and about 10,400 non-European ones, including around 31% in the United States, now fall under the environmental reporting rules of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), as reported by the Wall Street Journal.
This global shift underscores the deepening impact of Environmental, Social, and Governance on business and investment strategies.
ESG Investing: How It Works and Its Benefits
As we stated: ESG investing is more than a buzzword, it’s a strategy shaping the future of investments.
But what’s the driving force behind it?
Investors are increasingly using these criteria to screen and select investments, looking beyond financial returns to consider the broader impact of their investments.
According to NAVEX Global, 88% of publicly traded companies, 79% of venture and private equity-backed companies, and 67% of privately-owned companies had ESG initiatives in place.
The benefits? It’s not just about feeling good.
ESG investing often aligns with long-term returns. Companies with strong ESG practices tend to be more resilient, better positioned for long-term success.
Isn’t it compelling to invest in companies that not only grow financially but also contribute positively to the world?
Here’s a fact to ponder: according to a study by the International Finance Corporation, investments following Corporate Governance criteria showed higher financial and economic returns.
Challenges and Criticisms of ESG
We’re talking about a powerful concept, but it’s not without its challenges and criticisms. Let’s break them down:
- Measurement Difficulties: how do you quantify the unquantifiable? Measuring Environmental, Social, and Governance impact is complex due to its qualitative nature. This can lead to inconsistent and subjective interpretations of what good ESG performance looks like.
- Lack of Standardization: with various reporting frameworks and standards, there’s a lack of uniformity. Different companies might report differently, making it hard to compare and contrast Environmental, Social, and Governance performance across the board. Isn’t standardization crucial for clarity and comparability?
- Greenwashing Risks: some companies might claim to be more environmentally conscious than they actually are. This ‘greenwashing’ can mislead investors and consumers about a company’s true environmental impact. How do companies ensure authenticity in their Environmental, Social, and Governance claims?
- Data Inconsistency: the data can be inconsistent, incomplete, or hard to verify. This inconsistency can challenge the accuracy of Environmental, Social, and Governance assessments and decision-making.
- Balancing Act: striking the right balance in ESG initiatives is tricky. Are they too aggressive, risking business viability, or not aggressive enough, failing to make a significant impact?
Okay, let’s be real: these challenges are actually in our wheelhouse.
We’re aiming to dive deeper and provide a sturdier perspective on the market regarding the hurdles in implementing Environmental, Social, and Governance aspects.
In Capital Group’s latest study from October 2023, you can see some fascinating insights into this subject matter - definitely worth a look, check it out:

ESG vs. CSR: Learn the Difference
Understanding the distinction between ESG and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) is like comparing two sides of the same coin.
They’re related, but there’s a twist, check it out:
ESG, as we’ve discussed, focuses on a company’s operations and investment decisions in environmental, social, and governance areas. It’s quantifiable and often used by investors to screen potential investments.
Think of Environmental, Social, and Governance as the hard data driving investment decisions.
CSR, on the other hand, is more about a company’s efforts to improve society.
It’s how a company gives back, be it through philanthropy, community engagement, or ethical practices.
CSR initiatives are often self-set and self-reported, focusing on the company’s impact on society.
For example, a business donating to local schools or implementing fair trade practices in its supply chain falls under CSR.
So, while the first one is about integrating sustainable practices into the business model and measuring their impact, CSR is more about voluntary actions to contribute positively to society.
ESG Reporting and Compliance
Reporting is all about transparency and accountability. It’s how companies communicate their progress and commitment to Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria.
Think of it as a report card showing how well a company is doing in managing its environmental impact, social responsibilities, and governance practices.
So, what’s trending in Environmental, Social, and Governance reporting?
We’re seeing an increase in detailed disclosures. Companies are moving beyond just ticking boxes, they’re providing in-depth insights into their ESG initiatives.
This shift is driven by a growing demand from investors, customers, and regulators who want a clearer picture of a company’s Environmental, Social, and Governance performance.
Compliance standards are also evolving.
More rigorous and standardized reporting guidelines are being developed.
Companies are adapting by integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance into their core strategies and enhancing data collection methods.
They’re not just complying for the sake of it. They’re recognizing that good ESG performance can drive business success.
Case Studies: ESG in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples that already have significant impact.
TermoFisher
This company’s commitment to ESG has led to a 20% boost in efficiency, a 10% rise in revenue, and a 5% increase in shareholder value.
By joining the “Business Ambition for 1.5°C” campaign, TermoFisher is on its way to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Microsoft
Known for its tech innovation, Microsoft has also made strides in ESG.
Its focus on carbon neutrality and sustainable packaging has reduced its carbon footprint and waste generation.
Ikea
With its “People and Planet Positive” policy, Ikea ensures its operations benefit both humans and the environment, focusing on fair compensation, reducing environmental impacts, and promoting diversity and inclusion.
For instance, Ikea plans that 50% of the main meals offered in its restaurants will be plant-based by 2025.
Also, according to the Sustainability Report published in 2022, the company’s objective is to become fully circular by 2030.
Future of ESG: Trends and Predictions
As we gaze into the future of Environmental, Social, and Governance, it’s clear this is a field on the move.
In the past four years alone, the search for “ESG” has skyrocketed by 2,600%, according to a Harvard study. But what’s driving this surge, and where is it headed?
One key trend is the integration of advanced technology in Environmental, Social and Governance practices. Think AI and big data analytics being used to track and analyze metrics more accurately. This tech leap could revolutionize how companies monitor and report their efforts.
Regulatory changes are also on the horizon. As awareness of Environmental, Social and Governance importance grows, governments worldwide are likely to introduce stricter compliance standards. This shift will push companies to up their ESG game or risk falling behind.
Investor priorities are shifting too. According to Capital Group, a staggering 89% of investors now consider Environmental, Social, and Governance issues at some point in their investment process.
This indicates a growing understanding that ESG factors can significantly impact a company’s long-term viability and success.
How to Get Started with ESG
We know: starting with ESG can seem daunting, but it’s all about taking those initial steps.
For businesses ready to dive into the world of Environmental, Social, and Governance, here’s how to get the ball rolling:
- Assess Current ESG Performance: begin by understanding where you currently stand. What are your existing practices regarding environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance? This baseline assessment is crucial.
- Set Clear ESG Goals: what do you aim to achieve with your Environmental, Social, and Governance initiatives? Whether it’s reducing carbon emissions, improving labor practices, or enhancing transparency in governance, having clear, measurable goals is key.
- Develop a Strategy: now, how will you achieve these goals? This involves planning, resource allocation, and perhaps most importantly, ensuring that your Environmental, Social, and Governance goals align with your overall business strategy.
- Implement and Monitor: put your plan into action. But remember, this isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it deal. Regular monitoring and reporting on your Environmental, Social, and Governance performance are vital. Are you making progress towards your goals? If not, what adjustments need to be made?
- Engage Stakeholders: keep your stakeholders in the loop. Whether it’s employees, customers, or investors, their buy-in and feedback can be invaluable.
- Stay Informed and Adapt: this is a dynamic field. Staying informed about the latest trends and regulations and being ready to adapt your strategies accordingly is crucial.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, let’s reflect on the journey through the world of ESG.
This is about looking at the bigger picture, considering how environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and strong governance can drive long-term success and sustainability.
Why settle for the status quo when you can be part of something greater?
Think about it.
Embracing these principles isn’t just about doing good, it’s about smart, sustainable growth.
It’s an opportunity to innovate, to stand out, and to build a legacy that extends beyond financial performance. That’s what we’re talking about.
So, as we move forward in a world that increasingly values sustainability and ethical practices, the question isn’t if you should adopt Environmental, Social, and Governance principles, but… How quickly can you start?
The long-term benefits - for your business, society, and the planet - are too significant to ignore.
Let’s embrace Environmental, Social, and Governance and be part of shaping a brighter, more sustainable future.
ESG FAQ
How does ESG impact financial performance?
ESG impacts financial performance by mitigating risks and identifying sustainable opportunities. Companies with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance practices often experience increased investor interest, enhanced brand reputation, and long-term profitability, stemming from efficient operations and positive stakeholder relationships.
What are the best practices for ESG reporting?
Best practices for ESG reporting include maintaining transparency, ensuring accuracy and consistency in data, aligning with global standards like GRI or SASB, engaging stakeholders for feedback, and regularly updating reports to reflect the company’s ongoing Environmental, Social, and Governance efforts and progress.
What does ESG Mean?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It’s a framework used by companies and investors to evaluate a company’s impact on the environment, its social relationships, and how it is governed, impacting its ethical attributes and sustainability practices.
What are the 3 pillars of ESG?

The three pillars of ESG are Environmental (focus on a company’s ecological impact), Social (how a company manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and communities), and Governance (company’s leadership, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights).
What does ESG mean to employees?
To employees, ESG signifies working for a company that values sustainability, ethical practices, and social responsibility. It reflects a commitment to a positive workplace culture, fairness, inclusivity, and the overall well-being of the workforce and society.


